Using Learning Management Systems LMS for eLearning Content Delivery in Singapore
Using Learning Management Systems (LMS) for eLearning Content Delivery in Singapore
Introduction to Using Learning Management Systems LMS for eLearning Content Delivery in Singapore
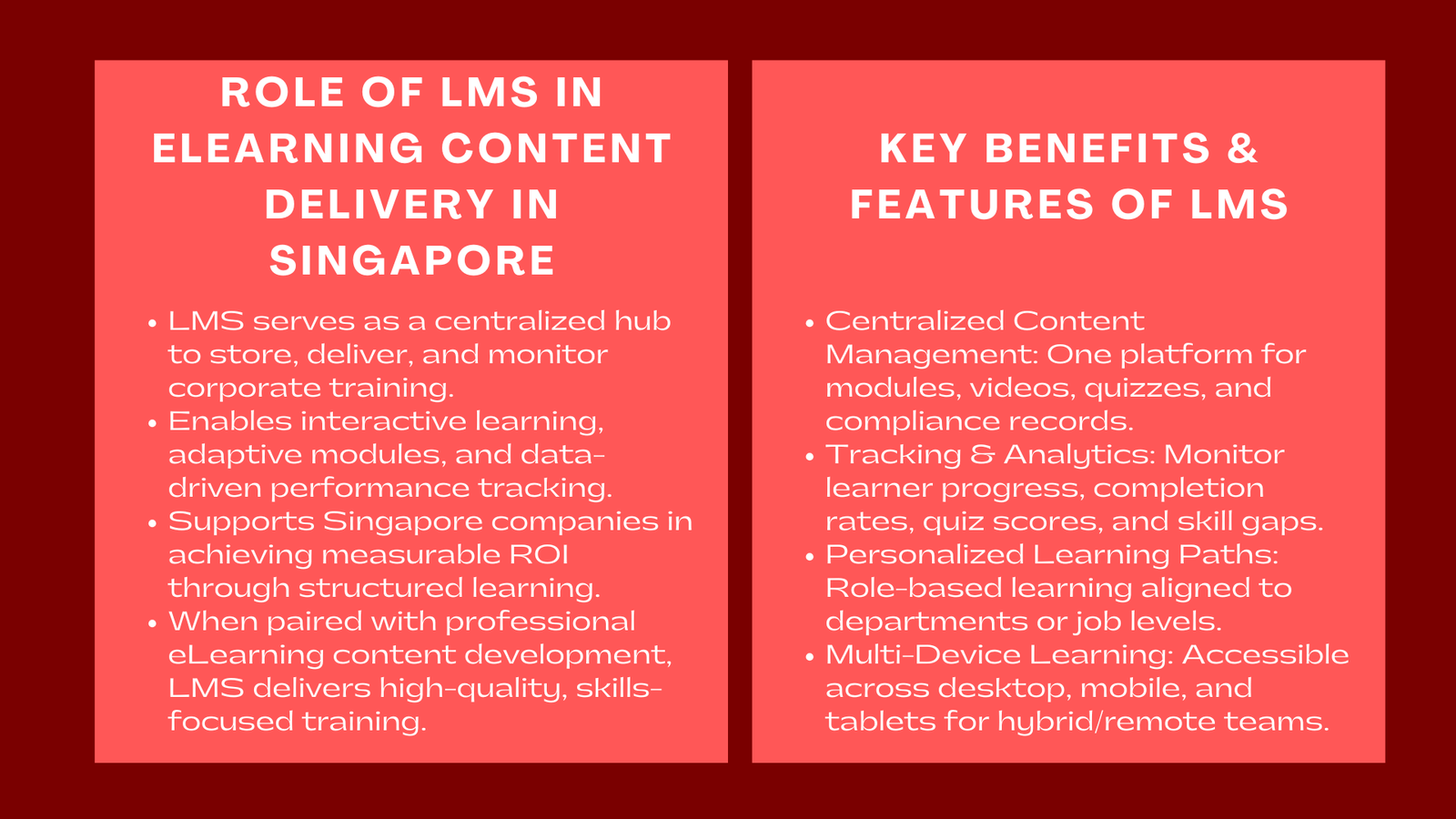
The Learning Management Systems (LMS) have emerged as the heart of successful eLearning in the present fast dynamic world of corporate learning. In the case of LMS in organisations in Singapore, it is effectively a one stop shop to control, monitor and improve training programmes. They allow the companies to store digital content, track the engagement of the learners, and create actionable insights that can be converted into measurable learning outcomes.
In addition to mere storing course materials, LMS resources are known to support interactive learning, adaptive learning, and performance tracking on the basis of analytics. This guarantees that the employees will get a well-organized and interactive learning process and the employer can be assured of the ROI of his training investment.
Combined with the services of a professional eLearning content development, an LMS enables using learning management systems for corporate training Singapore to provide high-quality and learner-focused programs. Such services aid in the creation of an interactive, engaging and business aligned content to ensure that knowledge is obtained together with practical skills by the learners. With the successful use of LMS, Singaporean companies can update the training process, improve the workforce performance, and develop the culture of lifelong learning.
Understanding the Role of an LMS
Centralized Learning Hub
Primarily, an LMS content delivery and analytics for eLearning effectiveness Singapore a single place of all training materials, such as interactive modules, video lessons, and quizzes, documentation and simulations. Such a centralization is the sole way to be sure of consistent provision of the same learning resources to the employees in various departments and locations.
As an example, a multinational company that has operational teams in Singapore, Malaysia, and Hong Kong can use the same LMS to host the compliance training and ensure that all the employees are provided with uniform content whilst making the process of regulatory audit of records less cumbersome. The centralized content is also helpful in the version control as it becomes simpler to update the material in case of the change of the policies or industry standards.
Sharing learning resources in an organization would mean saving on unnecessary duplication, simplifying of learning materials and employees have a clear and well structured learning process. This also is of benefit to HR and training administrators since they can effectively deal with onboarding, compliance and professional development programs on the same platform.
Tracking and Reporting Capabilities
The contemporary LMS systems are installed with powerful tracking and reporting services. Administrators are able to track the improvement of the learners, percentage of completion of each of the modules, the quiz results and time taken to complete certain courses. Such analytics can offer actionable intelligence which can help managers of training needs to define areas of skill deficiency, gauge interest and determine the approach to future training, especially when paired with interactive eLearning content services Singapore to enhance learner engagement and performance insights.
As an example, in case the documentation results in the employees having difficulties with a certain compliance module, the training team may introduce additional sessions or microlearning modules to deal with the gap in knowledge. In the same vein, talented students can be singled out in order to pursue higher training programs, to help them develop and grow in their careers.
This high level of reporting ensures that there is transparency and accountability in the corporate learning programs. Companies are able to create elaborate reports to the leadership, and that training programs help in producing quantifiable business outcomes and help in line business alignment.
Delivering Content Effectively
Personalized Learning Paths
The possibility to develop individual learning processes based on each employee, roles, or department can be described as one of the most significant advantages of an LMS. Tailor new learning will make sure that the employees are not wasting time learning something that does not relate to their duties; they will be able to target their areas of weakness and improve.
An example is in a financial services company where the first level of analysts can take a learning curve that focuses on the basics of accounting, senior analysts can take courses in risk evaluation and portfolio management. Creating personalized content based on the role of the learners enhances organizations in raising the levels of engagement, retention of knowledge and application of the skills in the workplace.
Multi-Device Accessibility
As remote and hybrid work-related arrangements gain more popularity, LMS systems give learners an opportunity to learn through the freedom of various devices: desktops, laptops, tablets, and smartphones. Employees are able to study at their own pace either when they are commuting or during breaks at lunchtime or at home.
The convenience will positively influence more engagement particularly amongst employees who might miss out on the sessions by the instructor because of conflicting schedules. Mobile accessibility also gives organizations the opportunity to implement just-in-time learning solutions which provide short-term microlearning modules or refresher content at the point when it is actually required by the employees.
Enhancing Engagement
Interactive and Gamified Elements
The engagement aspect is extremely important with regard to effective eLearning programs. Gamifications, simulations, quizzes, and the usage of interactive features often make LMS platforms turn passive contents into active learning.
As an illustration, the staff who have completed a cybersecurity training module can take part in a simulation during which they can learn to detect possible phishing attacks in the real world. Learners can be motivated to study actively by means of gamified quizzes that have scoring, badges, and leaderboards to refresh important points.
The interactive elements assist the learners to have a better retention of whatever they learn because of his combination of theory and practice. This leads to an increase in the completion rates, improvement of skills and confidence in being able to handle job tasks.
Social Learning Features
An LMS has social learning characteristics, which promote teamwork and sharing of knowledge among peers. Group projects, chat forums, discussion boards and collaborative challenges promote the spirit of community and help to teach each other to the employees.
An example of this is a marketing team working on a virtual campaign project, where people talk about the strategies, support each other via the use of resources, and receive a comment regarding the work. Social learning can also increase the engagement and as well as help to retain and improve again and again so as to establish a culture where learning becomes a collective and collaborative part of the culture.
Integrating Assessments and Feedback
Continuous Assessment Strategies
LMS environments facilitate the use of both formative and summative evaluations that are interwoven with the study. Constant evaluation offers to the learners real-time feedback so that they can know the errors they make and rectify them even as the lesson goes on.
As an example, employees could undergo a small quiz after the completion of a workplace safety module, and the scoring will be instant, and the answers should be explained to them. This will help to strengthen the learning process and make the employees be able to utilize knowledge in a real-life environment. Continuous assessment is also used to enable instructors and administrators to monitor.
Feedback Loops
LMS allows the ability to create a closed feedback process between students, teachers and management. Individual performance feedback can be provided to the learners, whereas the instructors can obtain the data on the course effectiveness and course quality.
The survey or ratings that the administrators can gather at the end of the courses will help in improving course content and meeting the needs of learners. This recursive process also guarantees on-going enhancement such that the training programs remain relevant and involving and meeting the changes in the business needs.
Measuring Training Effectiveness
Learning Analytics and KPI Tracking
Another of the strongest features of an LMS is that it allows measuring training effectiveness with the help of analytics. The rate of course completion, the degree of engagement, quiz results, and time to complete each module are metrics used to give the overall picture of the performance of the learners.
An example that can illustrate this is when the engagement in a leadership development course is low the administration should deduce whether the complexity of the content, the length of the modules, or the mode of delivery is interfering with the participation of the learners. Data-driven decisions with the use of analytics will allow organizations to make decisions based on data to constantly streamline training programs.
Linking Learning to Business Outcomes
In addition to the performance of the individual learners, the LMS platforms help organizations relate training information to the overall business performance, including improved productivity, sales statistics, regulatory compliance, or satisfied customers.
As an illustration, KPIs to be tracked after training of sales training programs may show an increase in conversion rates or improved relationships with the clients caused directly by an increase in the skills. By being able to tie learning to quantifiable business outcomes, the organizations can make training expenditures worthwhile and be able to prove ROI.
Choosing the Right LMS
Scalability and Customization
It is necessary to pick an LMS that will be able to scope with the growth of the organization. The system is to be supported by increasing user numbers, changing content demands, as well as various learning tracks. The options of customization give the chance to brand, set learning goals, and processes and match to the needs of the company, promoting quicker user adoption and interest.
Integration with Other Systems
A successful LMS must easily connect to the HR management systems, performance management software, and communication software among other enterprise software. Integration guarantees easy user experiences, ease of tracking and a comprehensive perspective of development of every employee in the organization.
Best Practices for LMS Implementation
Pilot Testing
Pilot testing of a small group is a requirement that enables the detection of possible technical problems, usability problems, and gaps in the content before the implementation of LMS on an organizational-wide scale. Pilot user feedback helps in changes and facilitates a more successful implementation in full scale.
Continuous Improvement
An LMS is not something that can be set and forgotten. At regular intervals, changing the content, reviewing the interaction statistics, and adding the comments of learners will help keep the platform topical, productive, and interesting. The other factor that helps an organization to remain flexible in a changing business world is continuous improvement.
Conclusion
LMS is an essential learning instrument that can be used to implement effective, engaging, and measurable eLearning programs in Singapore. The organizations can extend their content focus, individualization of learning, encompassing both interactive and social facilities, and analytics as a means of improving the experience of learners and the effectiveness of training.
LMS platforms can also be used along with professional services of developing eLearning content to create comprehensive, structured and outcome-oriented training programs. Effective implementation, constant enhancement, and evidence-based practices are the reasons why eLearning programs can contribute to the achievement of real business outcomes, the development of the employee base, and the creation of a culture of lifelong learning at the business level.