How to Design Engaging LMS E-Learning Content Effectively
How to Design Engaging LMS E-Learning Content Effectively
Introduction to LMS Content Development
The concept of Learning Management Systems (LMS) has proved to be the heavier part of the modern training and education delivery by corporations, places of learning, and even independent educators. Regardless of an intention to train people, onboard new employees, upskill teams, or provide academic courses, the success of the learning consolidation depends on the quality of LMS content. Interactive finance training course Singapore also plays a vital role in ensuring practical knowledge transfer, while the benefits of employee training programs highlight the value of well-structured LMS content for both organizations and learners.
When implemented effectively, a properly built LMS content plan not only keeps the learners engaged; it also helps make sure the content is instructionally sound and compliant. Designing, constructing, accessing, and evaluating the content is not a simple procedure of filling in anything in an LMS. Using best practices, organizations are able to optimize the degree of learner engagement, retention, and performance.
The content that can be contained in an LMS is varied and can include videos, interactive quizzes, simulations, case studies, documents and more. The variety of format implies that the developers should not overlook the features of the platform and needs of the learners. As has been pointed out, effective LMS content creation is achieved when the learning objectives are aligned with the relevant principles of the instructions design, management of consistency is ensured and feedback is received to further the improvements.
Understanding Learner Needs and Defining Objectives
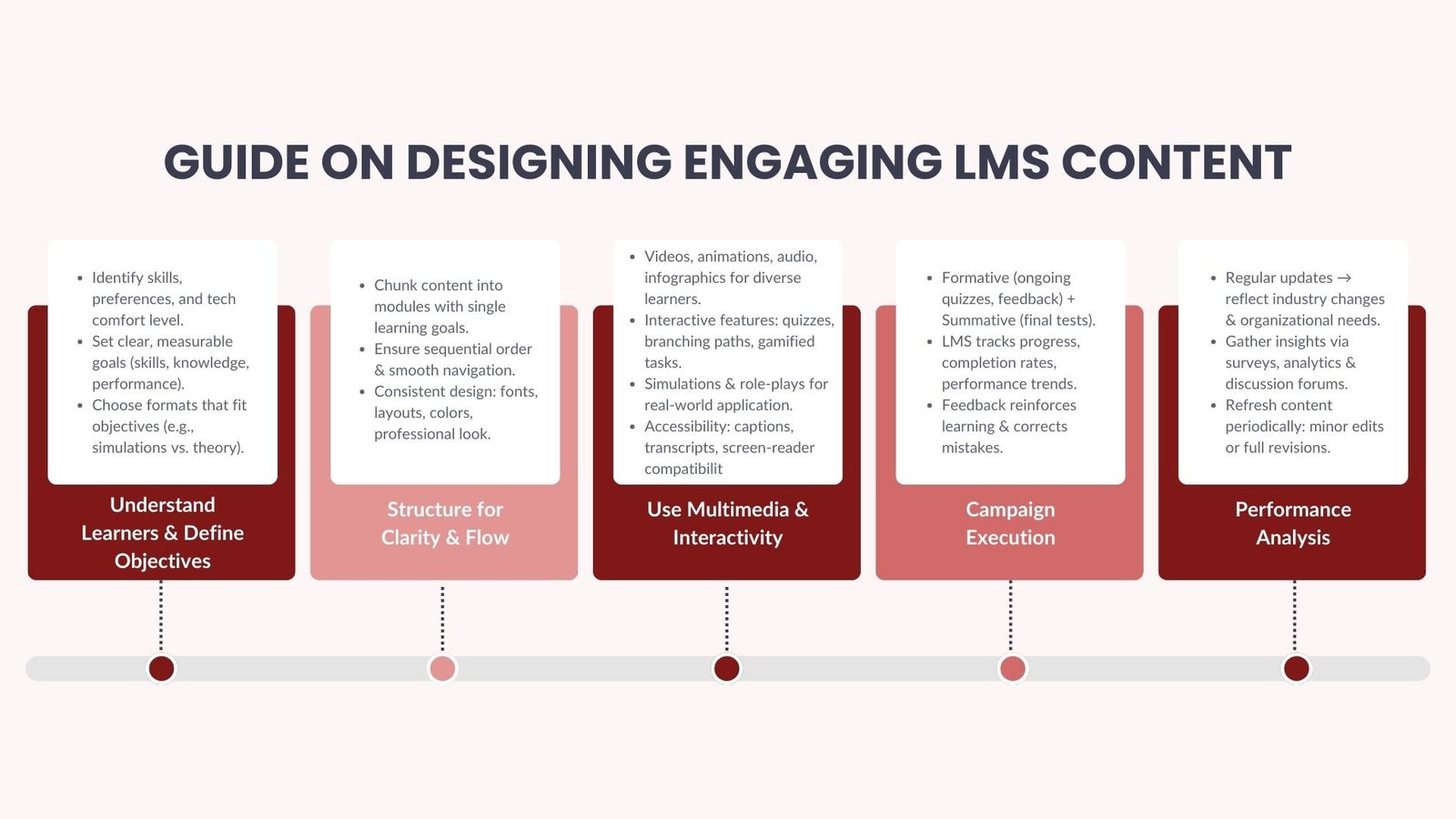
Knowledge of the audience is the beginning point of quality LMS content development. Even a well-produced content can still fail to offer any sense of engagement, unless a clear understanding of who the learners are, their current levels of skills, their learning preferences and their level of comfort with technologies is established. A formal course on environmental science will bear no resemblance at all to a sales training module that is conducted in a corporation. The emphasis may differ in the corporate and the academic world, with one group being practical application and a gain in skills, and the other group focusing on reasoning and theory.
Learning objectives have to be defined prior to the start of the content developments. Goals serve as the blueprint and form the selection of the format of the contents, the tone and evaluation practices. In other words, when the goal is to make employees capable of working with a new software system, step-by-step interactive training or simulations could be more effective as compared to long theoretical seminars. Goals must be quantifiable that can be monitored either in form of quizzes, assignments or performance indicators in the LMS.
Structuring Content for Maximum Engagement
The content design of LMS plays an important role in impacting the behaviour of learners to interact and remember the information. Chunking can be used to contain the cognitive overload and does not stress the learners to take in large amounts of information at one go. All modules ought to have one learning goal address them and have a sequential order. As an example, a compliance training course could begin with an overview of the regulations, after which one dives into some details of the policy, and then to practical cases and scenarios.
Visual design is very important in the organization of the content. Messy layout or disparity in formatting may be a distraction to learning, and demand decreases. The same fonts, colors, and layout styles throughout the LMS create a professional and stringent learning environment. The complex concepts can also be explained and illustrated with the help of graphics and diagrams, and use of infographics and animations can assist in that as well. Moreover, the LMS has clear navigation that enables the learners to easily refer to their progress and revise when the need arises.
An option that draws and makes content structuring effective is a system of interactive elements. The quizzes at the end of modules, decision-making scenarios, and branching pathways that adjust, depending on the responses of the learner, would help in involvement and memory retention. Interactivity should be balanced with instructional clarity since the learning process may get distractive through activities.
Incorporating Multimedia and Interactivity
Even in the digital learning environment of the modern world, text-based content is often insufficient to maintain the interest of the learners. The videos, audio narrations, animations, and simulations, which are multimedia elements, have the ability to address various learning styles, and thus make the content more accessible and memorable. It would be inefficient to sit pages of writing that explain a complex process whereas a short video explainer would do a better job at that, whereas some learners that rely on audio-based instructions will also have access to audio narration.
Interactivity is not quiz-based only but incorporates complex tasks like simulations, drag-and-drop exercises, role-play to various extents, and gamified challenges. These factors prompt the audience to be active instead of passive recipients of information. An example would be a leadership development course, where a simulated working scenario involving a conflict situation could occur and the learner be offered alternative options in dealing with this conflict with different strategies given as possible outcomes of the selected action.
Multimedia integration should include accessibility as a matter of concern. This involves the scenic provision of video transcripts, audio captions, and compatibility with assistive application. The idea is to ensure that the learning material is inclusive of all the learners irrespective of whether they are physically impaired or have learning preferences. Accessibility is not merely a question of compliance but also an ethical requirement showing the dedication of the organizations towards equal learning chances.
Assessing and Measuring Learning Outcomes
Evaluation of the LMS content is an essential element of the content production since the evidence of learning success and efficiency can be measured. The course objectives that have been outlined are strictly related to effective assessment strategies. In case it is necessary to teach procedural skills, the most appropriate evaluation can be practical demonstrations or simulations. Multiple-choice questions or written reflections should be more appropriate, however, in case of conceptual understanding as the target.
The assessments can be inserted anywhere in the course of LMS. The formative assessment within the learning process will permit discovering the gaps in knowledge early on letting learners review the material without passing to the next one. Summative assessment is conducted at the close of the module or course to test the level of the learner on the material. LMS is also able to monitor metrics about completion rates, time consumed solving modules, and trends in performance, which will be of good use to the standalone instructors and administrators.
Feedback is vital in the assessment procedure. Instant and positive feedback assists students in learning wrongs and reinforcing the right knowledge. Take as an example using a quiz where a learner enters an incorrect answer, the LMS is capable of providing a brief explanation to lead a learner back to the proper concept. The process of continuous monitoring and periodic reassessment is necessary so that learning could be retained and skills updated.
Continuous Improvement and Content Updates
Updating of content within a short period and with ease is considered as one of the merits of digital learning platforms. This adaptability enables the organizations to keep up to date changes in the industry, legal changes or what change in an organisational strategy. Obsolete information reduces credibility, and may even prove misinformed in areas where there are frequent changes in rules or good practice.
The continuous improvement would entail obtaining the comments of learners and instructors. The tool that could aid in this is surveys, discussion forums and analytics on LMS to understand what modules are interesting and what areas are confusing and whether learners practice the knowledge in the real world. Upon analyzing these insights, course creators will be able to streamline the materials, clarify parts that are unclear and optimize interactivity, where necessary.
Editing content ought to be a repetitive process and not just a singular process. Reviewing and refreshing materials on a regular basis leads to updating courses to a large extent. Occasionally, revisions that are relatively minor, like scrapping of old examples or the updating of statistics, may be adequate where as in other instances a thorough reworking may be necessary to conform to new goals or technological potentials.
Conclusion: Building Impactful LMS Learning Experiences
Effective LMS content needs a combination of instructional design skills, technological knowledge and the desire to keep improving it on an ongoing basis. Organizations can engage and deliver effective learning experiences by commencing with definite learning goals, organizing the learning in the logical sequence, multimedia and interactivity, and staying directed at evaluation. The process does not stop after content is published, but develops with help of feedback from learners, new technologies, and educational requirements.
The best practices in creating LMS in content will eventually help all stakeholders. The learners receive appealing, accessible, and relevant content that favours development. Educators have solid information to depend on to carry out the teaching effectively, as organizations benefit in terms of enhanced performance, adherence, and knowledge preservation among uniformed staff. Made with a purpose, the process of creating LMS content can be defined as a strategic investment that leads to the individual development as well as the success of the entire organization. Interactive e-learning content creators Singapore further support this process by providing innovative and engaging learning solutions.