Blended Learning Solutions Combining eLearning with Classroom Training
Blended Learning Solutions: Combining eLearning with Classroom Training
Introduction to Blended Learning Solutions Combining eLearning with Classroom Training
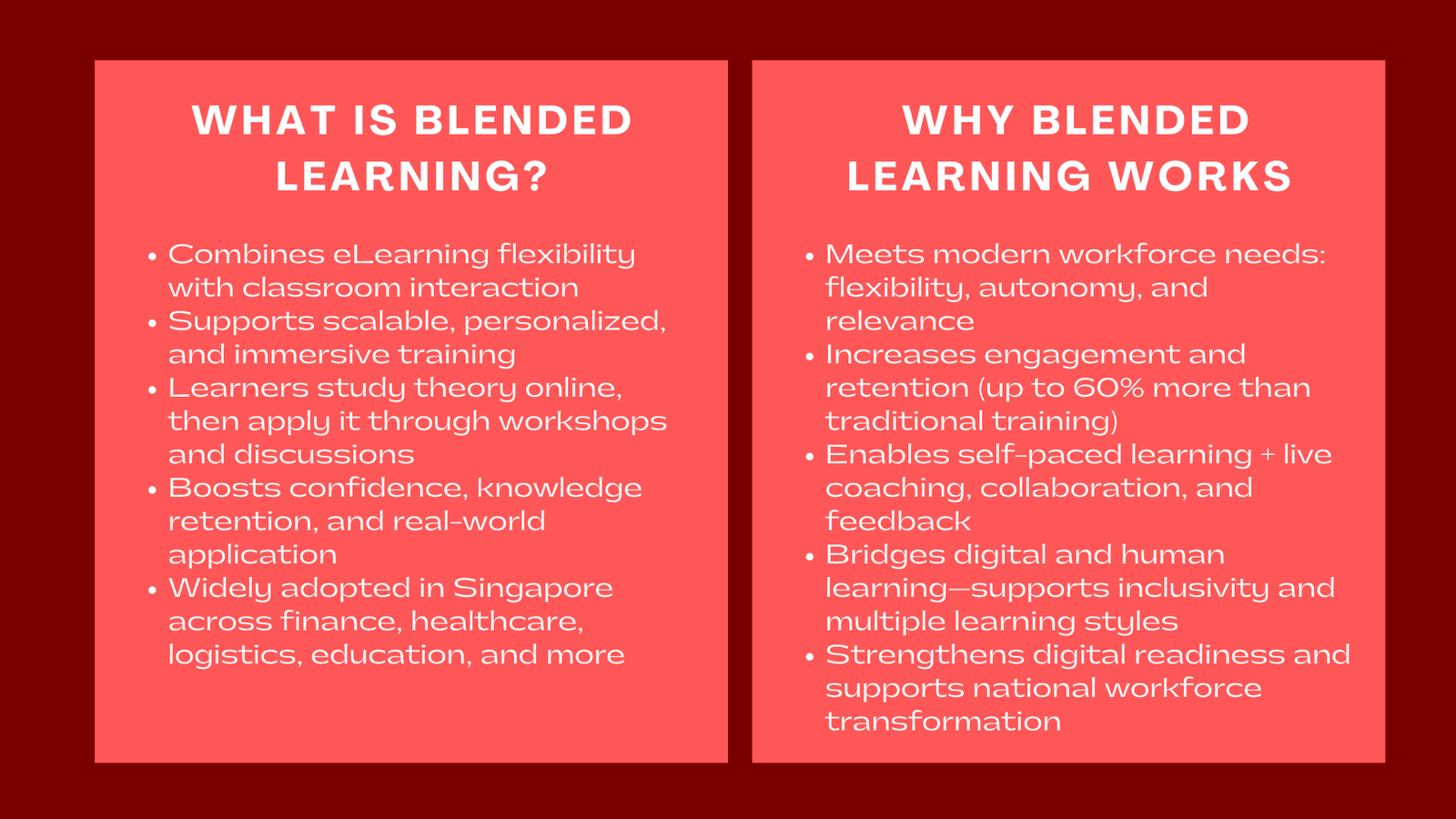
As organizations and educational institutions adapt to a post-digital world, blended learning has emerged as one of the most effective models for sustainable, scalable, and personalized training. By combining the strengths of eLearning — including flexibility, accessibility, consistency, and interactive multimedia content — with the human interaction and collaboration inherent in classroom instruction, blended learning delivers a balanced and immersive learning experience.
In the corporate sector, this model is transforming professional development by allowing learners to master theoretical concepts independently through digital platforms, then apply them practically through workshops, coaching sessions, or facilitated discussions. This dual approach not only reinforces learning but also provides employees with the confidence to apply knowledge in real-world scenarios. For educational institutions, blended learning bridges the gap between online delivery and traditional classroom engagement, ensuring both convenience and depth of learning. It supports self-paced study while maintaining the benefits of peer-to-peer interaction, mentoring, and immediate feedback.
In Singapore, blended learning solutions for corporate training have gained significant momentum across multiple sectors, including finance, healthcare, education, manufacturing, and logistics. National initiatives such as SkillsFuture Singapore (SSG) and the Institute for Adult Learning (IAL) actively promote blended approaches as part of lifelong learning and workforce transformation strategies. These initiatives encourage organizations to adopt learning models that are not only scalable but also adaptable to rapidly changing industry demands, thereby aligning workforce skills with Singapore’s economic priorities.
The Relevance of Blended Learning
Addressing Modern Workforce Needs
Modern learners increasingly value autonomy, flexibility, and relevance in their learning experiences. Blended learning enables self-paced eLearning modules complemented by live sessions for interaction, coaching, and problem-solving. This hybrid structure aligns with the lifestyles of professionals who balance work responsibilities with learning commitments, ensuring that training is both practical and achievable without disrupting productivity.
A Singapore-based bank implemented a blended leadership program that combined online theory modules with biweekly live workshops. Attendance rates rose to 98%, and post-training performance evaluations showed a 32% improvement in leadership competencies. Employees reported that the combination of self-paced learning and interactive workshops allowed them to internalize concepts more effectively than through classroom training alone, demonstrating the growing impact of blended learning content Singapore in corporate development.
Blended learning also addresses generational differences in learning preferences, accommodating younger employees who are digitally native while still providing structured, guided learning for those who prefer in-person interactions.
Enhancing Knowledge Retention and Engagement
Research, including findings published in the Journal of Educational Psychology, shows that learners retain 25–60% more information through blended learning compared to traditional face-to-face instruction alone. This is due in part to the spacing effect, where revisiting material across different formats and time intervals improves memory consolidation.
Blended learning extends learning beyond the integrated eLearning and classroom training Singapore, enabling learners to reflect, apply, and revisit key concepts at their own pace. For example, participants in a blended finance course might watch an eLearning module on risk assessment, complete interactive quizzes, and later apply their understanding in group problem-solving exercises. The combination of repetition, application, and discussion reinforces knowledge retention and fosters higher engagement levels than single-mode learning experiences.
Supporting Digital Transformation and Inclusivity
Blended learning drives digital readiness by familiarizing employees with online platforms, multimedia tools, and self-directed learning behaviors. In Singapore, this supports government-led initiatives for digital inclusion, ensuring equitable access to lifelong learning opportunities across all industries and professions. It also prepares organizations for future work scenarios, where hybrid models and remote collaboration are increasingly prevalent.
By integrating digital tools and collaborative learning, blended programs ensure that no employee is left behind, catering to different learning speeds, accessibility needs, and technological comfort levels.
Core Components of Blended Learning
Online Self-Paced eLearning
Online self-paced eLearning includes digital modules, instructional videos, quizzes, simulations, and interactive assessments that learners can access anytime and anywhere. This component primarily focuses on foundational theory, conceptual understanding, and knowledge acquisition.
Learners progress at their own pace, accommodating individual schedules. Standardized content ensures consistency and uniform knowledge transfer across teams. It can be updated easily to reflect policy, regulatory, or procedural changes. A healthcare organization in Singapore used self-paced compliance modules for all clinical staff. Completion rates reached 100% within two weeks, a milestone that previously required multiple in-person sessions over several months. The online modules allowed staff to review procedures multiple times, reinforcing adherence and understanding.
Instructor-Led Training (ILT)
Instructor-led training, whether conducted in-person or via live virtual platforms, provides learners with the opportunity to deepen understanding through dialogue, collaborative exercises, and direct feedback. This stage emphasizes practical application, interpersonal skills, and real-time problem-solving.
Workshops should follow digital pre-learning modules closely to ensure participants arrive prepared. This sequencing allows learners to immediately apply theoretical knowledge, ask clarifying questions, and engage in meaningful discussions, increasing the overall effectiveness of the training.
Collaborative Learning and Discussion Forums
Social learning is a critical component of blended programs. Online discussion boards, peer feedback loops, and collaborative projects allow learners to engage with real scenarios, exchange insights, and co-create knowledge.
A Singaporean logistics firm integrated Slack-based discussion channels for its blended learning program. Peer interaction increased by 60%, and employee satisfaction surveys indicated improved teamwork and communication skills. Collaborative learning encourages reflective thinking, deeper engagement, and a sense of accountability among learners.
Assessment and Feedback Loops
Blended programs often incorporate a combination of automated digital quizzes and live assessments. This combination provides both immediate feedback and nuanced insights from instructors, allowing learners to identify strengths and areas for improvement. Continuous feedback loops help maintain engagement, correct misunderstandings promptly, and reinforce learning objectives.
Continuous Learning Pathways
Effective blended learning extends beyond single courses. Learners receive ongoing digital resources, microlearning updates, case studies, and optional modules that reinforce knowledge over time. Continuous pathways encourage employees to maintain skill development as an ongoing process, rather than a one-time event, supporting lifelong learning and career progression.
Implementation Strategies for Blended Learning
Align Learning Outcomes with Delivery Mode
Each module should match its learning objectives with the most effective delivery medium. Digital eLearning is ideal for theoretical knowledge, policy understanding, and procedural training, while classroom or live sessions work best for practical application, teamwork, and immediate feedback. Aligning delivery modes ensures that each component contributes meaningfully to overall competency development and measurable outcomes.
Curriculum Mapping and Modular Design
Blended learning programs should be designed as a continuous journey rather than isolated modules. Mapping online and offline components sequentially — pre-learning, live training, and post-learning reflection — mirrors Singapore’s National Skills Framework approach, emphasizing skill progression and applied competence.
Trainer Upskilling and Digital Facilitation
Trainers play a pivotal role in blended learning success. They must transition from traditional lecturers to learning facilitators, capable of integrating digital tools, managing interactive sessions, and fostering inclusive learning environments. Train-the-trainer programs focusing on virtual facilitation, breakout room management, polls, simulations, and real-time analytics enhance trainer effectiveness.
Learner Support and Accessibility
Comprehensive onboarding ensures that learners are familiar with LMS navigation, digital tools, and troubleshooting procedures. Accessibility features such as closed captions, multilingual content, adjustable text sizes, and device-agnostic design support inclusivity, ensuring all learners can participate fully.
Data-Driven Program Evaluation
Learning Management Systems enable organizations to track completion rates, quiz scores, engagement levels, and learner satisfaction. Adopting Kirkpatrick’s Four-Level Evaluation Model allows organizations to measure learner satisfaction, knowledge acquisition, application on the job, and organizational performance impact.
Strategic and Analytical Thinking through Blended Learning
Enhancing Decision-Making and Problem-Solving
Case study workshops following digital modules allow learners to apply theoretical frameworks to real-world problems. For example, after completing an online finance course, participants may analyze an actual company’s balance sheet in a live workshop setting, developing critical thinking and analytical skills.
A Singaporean investment firm implemented blended sessions for ESG reporting training. Analysts applied digital pre-learning concepts to real market data, resulting in a 25% improvement in analytical accuracy.
Promoting Reflective and Collaborative Learning
Post-class reflections encourage learners to internalize insights and relate them to their daily work. Group discussions simulate boardroom decision-making, enhancing leadership, communication, and collaboration competencies. Reflective learning strengthens the connection between theory and practice, creating more impactful outcomes.
Real-Time Analytics for Continuous Improvement
Integrated analytics dashboards allow facilitators to monitor engagement, identify struggling learners, and adjust session content dynamically. This iterative approach ensures alignment with learning objectives and maximizes participant engagement while maintaining program quality.
Technology Integration in Blended Learning
Learning Management System (LMS) Integration
A centralized LMS, such as Moodle, Canvas, or SAP SuccessFactors Learning, anchors the blended learning ecosystem. It organizes digital content, schedules live sessions, tracks attendance, and generates performance reports. Automated features like reminders, discussion forums, live chats, and assessment tracking streamline administration and enhance learner experience.
Learning Experience Platforms (LXP)
LXPs such as EdCast, Degreed, or Cornerstone leverage AI to curate personalized learning paths, deliver social learning feeds, and recommend content aligned with career development goals. LXPs place learners at the center of the learning experience, increasing motivation and engagement.
Virtual Classroom Technologies
Platforms like Zoom, Microsoft Teams, and Webex Training enable live, synchronous learning with breakout discussions, interactive polls, and Q&A sessions. Integrating these tools with LMS platforms ensures seamless tracking of attendance, participation, and engagement.
Artificial Intelligence and Automation
AI-driven systems analyze learner patterns, predict disengagement, and provide real-time interventions. Chatbots can answer common queries instantly, while automated recommendations guide learners toward relevant content.
A Singapore university deployed an AI chatbot to manage scheduling and FAQs for blended courses, reducing administrative workload by 40% and improving learner satisfaction.
Mobile and Cloud Accessibility
Mobile-friendly design ensures learners can access digital modules anytime, anywhere. Cloud infrastructure guarantees scalability, centralized storage, and real-time synchronization across devices — critical for remote teams and multinational organizations.
Advantages of Blended Learning
Blended learning offers flexibility, allowing learners to control when and how they engage with content. It scales efficiently across distributed workforces, reduces costs associated with travel and physical venues, and combines the engagement of digital tools with human interaction. Repetition and reflection improve retention, while personalized pacing accommodates diverse learning styles. Continuous data-driven evaluation ensures ongoing optimization, and accessibility features promote inclusivity for all participants.
Conclusion
Blended learning is more than the sum of online and classroom training; it is a strategic convergence of technology, pedagogy, and human connection. By leveraging the scalability and interactivity of digital platforms with the immersive engagement of live instruction, organizations create dynamic learning ecosystems that support lifelong development and measurable outcomes.
In Singapore’s progressive corporate and education sectors, blended learning represents the future of workforce development — agile, inclusive, and data-driven. As industries evolve and workforce expectations shift, this approach ensures that learning remains both human-centered and technologically empowered, preparing individuals and organizations for sustained success in a post-digital world.