Interactive eLearning Content Boosting Knowledge Retention
Interactive eLearning Content: Boosting Knowledge Retention
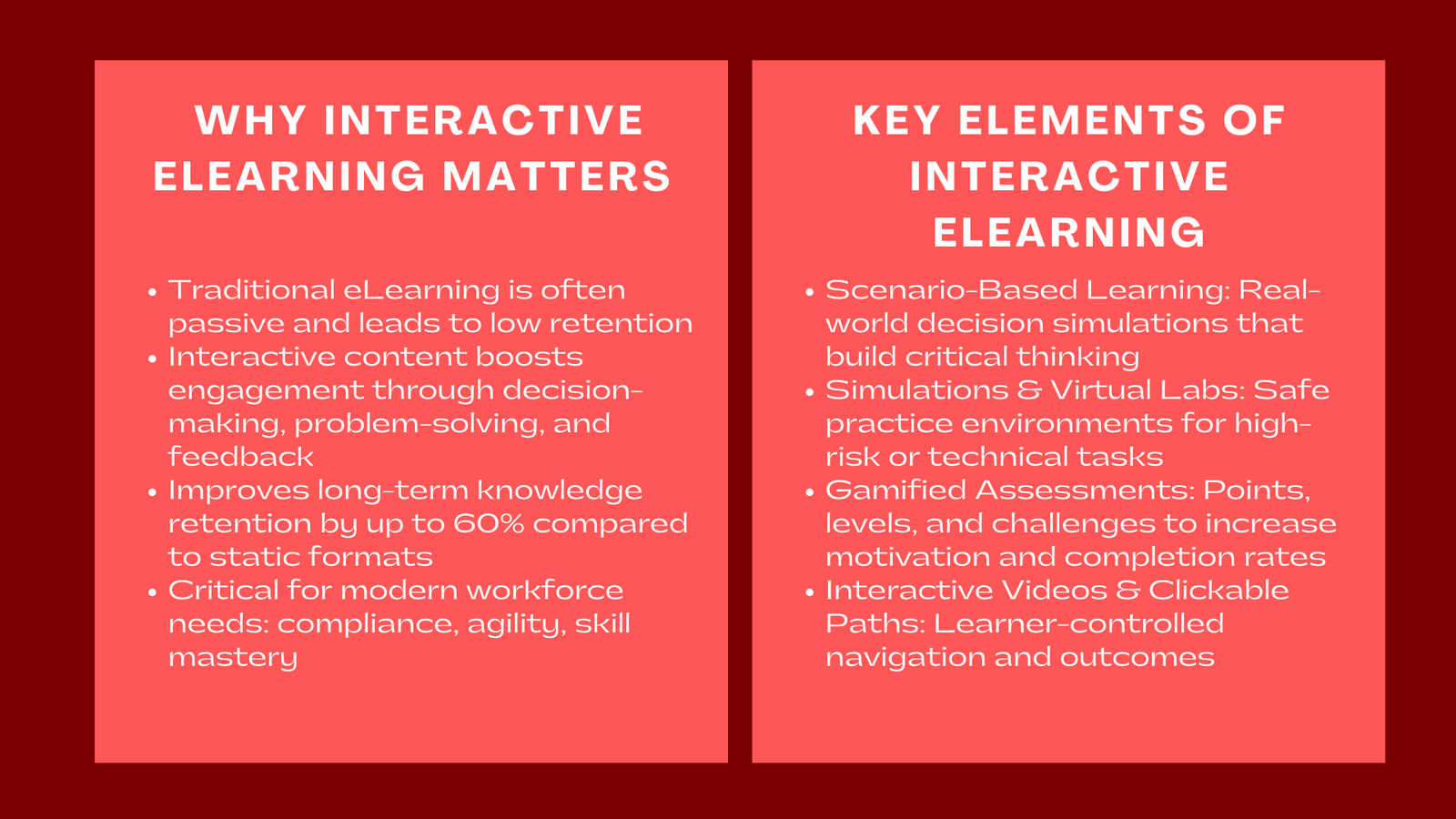
In today’s fast-paced digital learning environment, interactivity has emerged as the defining feature that separates passive knowledge consumption from active understanding. Traditional eLearning, which often relies heavily on static slides, PDF documents, and one-way video presentations, has struggled to capture learner attention consistently and maintain long-term retention of information. Many learners report feeling disengaged or overwhelmed by traditional formats, which do not provide opportunities for immediate application or reflection.
Interactive eLearning content transforms the learning experience by allowing learners to participate actively, practice critical thinking, and apply their knowledge in simulated environments. Instead of passively observing, learners are encouraged to make decisions, solve problems, and explore multiple outcomes, which enhances engagement and knowledge retention. This shift is particularly relevant as organizations increasingly prioritize workforce agility, compliance accuracy, and continuous professional development, especially when supported by custom eLearning content development Singapore for corporate training. Modern learning initiatives no longer focus solely on delivering content—they aim to produce measurable outcomes, including skill mastery, behavioral change, and operational efficiency.
In Singapore, where regulatory compliance, financial precision, and digital transformation are critical competitive advantages, interactive eLearning is more than a training tool—it is a strategic investment. Corporations, government agencies, and educational institutions are integrating interactivity into their training programs to meet regulatory requirements, nurture human capital, and align with national initiatives such as SkillsFuture. Interactive learning helps employees not only understand information but also apply it effectively, fostering measurable improvements in performance and decision-making capabilities.
The Relevance of Interactive eLearning in Modern Learning Design
The Shift from Passive to Participatory Learning
Research consistently demonstrates that learners retain information more effectively when they actively engage with content. Passive methods, such as reading documents or watching lectures, often lead to limited comprehension and short-term memorization. Interactive eLearning, on the other hand, transforms learning into a two-way process. Learners can test concepts, reflect on outcomes, and adjust their strategies based on immediate feedback.
For example, instead of reading a compliance policy document, learners might navigate a branching scenario that simulates real-world decision-making. Each choice leads to unique consequences, allowing learners to understand the cause-and-effect relationships between decisions and outcomes. This method encourages learners to experiment in a safe environment and internalize the reasoning behind their actions. By engaging visual, auditory, and kinesthetic learning pathways simultaneously, interactive content ensures that information is processed at a deeper cognitive level, which significantly improves long-term retention. Studies from the eLearning Guild indicate that interactive content can increase knowledge retention by up to 60% compared to static formats.
Alignment with Corporate Learning Culture
Corporate learning today emphasizes employee empowerment, self-directed learning, and a culture of continuous improvement. Interactivity fosters ownership by enabling employees to actively engage with the material, explore different scenarios, and experiment with solutions in a controlled environment. In Singapore’s high-performance industries such as finance, healthcare, and logistics, where operational accuracy and regulatory compliance are paramount, interactive eLearning allows employees to rehearse complex decisions without risk. This reduces real-world errors, promotes confidence, and cultivates a growth mindset among learners.
Interactive learning also aligns with corporate values of agility and innovation. Employees who can experiment safely and learn from failures are better equipped to navigate dynamic market conditions and adopt emerging technologies. By integrating interactive modules into corporate training, organizations create a workforce capable of critical thinking, problem-solving, and adaptive learning.
Core Components of Interactive eLearning Content
Scenario-Based Learning
Scenario-based learning is a powerful tool that immerses learners in realistic challenges requiring critical decision-making. Each decision within a scenario triggers specific outcomes, simulating the consequences of real-world actions. For instance, a Singapore-based logistics company developed a branching scenario for operations managers to manage shipment delays. Learners navigated complex factors such as client communications, penalty risks, and resource allocation decisions. This interactive approach improved situational judgment, decision-making speed, and reduced escalation cases by 25%.
scenario-based and gamified eLearning platforms Singapore learning enhances cognitive skills, including critical thinking, empathy, and problem-solving. It encourages learners to consider multiple perspectives, anticipate outcomes, and weigh alternatives. By creating a realistic context, scenario-based learning also fosters a stronger emotional connection to the content, which further enhances memory retention and skill application.
Simulations and Virtual Labs
Simulations and virtual labs provide learners with the opportunity to practice in environments that replicate real-world conditions without requiring physical resources or exposing participants to risk. In finance, learners can simulate trading environments to understand market behavior and decision-making under pressure. In manufacturing or energy sectors, virtual labs allow employees to operate complex equipment, troubleshoot errors, and practice emergency response protocols.
For example, a Singapore energy company implemented 3D safety simulations to train technicians on emergency response procedures. The simulations allowed technicians to practice handling hazardous situations repeatedly, resulting in a 40% improvement in readiness assessment scores. This type of experiential learning helps employees develop procedural memory, build confidence, and significantly reduces the cost and risk associated with live training exercises.
Gamified Assessments
Gamification turns traditional quizzes and assessments into engaging, goal-oriented experiences. By incorporating elements such as points, progress bars, challenges, and real-time leaderboards, learners are motivated to participate actively while receiving immediate feedback. For example, a major Singaporean bank implemented gamified compliance refresher training, turning standard policy quizzes into mission-based challenges. Within three months, course completion rates increased from 68% to 94%.
Gamified assessments encourage repeated practice, foster mastery, and allow organizations to collect measurable performance data. They create a competitive yet supportive learning environment that drives engagement, motivates learners to improve, and promotes self-directed skill development.
Interactive Videos and Clickable Learning Paths
interactive eLearning solutions for corporate training Singapore offer learners the ability to make choices, click on embedded hotspots, and explore alternative outcomes. This approach is particularly effective for storytelling-based training, including leadership, ethics, and customer service. A Singapore healthcare provider launched interactive patient scenario videos for nurses, where decisions about medication, communication style, and escalation protocols influenced the storyline. Post-course surveys revealed a 92% satisfaction rate and measurable improvements in patient communication and care quality.
Interactive videos enable learners to visualize complex scenarios, understand consequences, and experience situations they may not frequently encounter in real life. By giving learners agency in the story, this approach also improves engagement and reinforces decision-making skills.
Drag-and-Drop and Matching Exercises
Drag-and-drop exercises help learners internalize processes, classifications, and sequencing tasks. Learners can arrange workflow steps in proper order, match terminologies with definitions, or categorize information. This type of interactivity promotes active recall, strengthens retention of technical content, and appeals to visual learners. Over time, repeated exposure to drag-and-drop exercises reinforces procedural knowledge and ensures learners are capable of executing tasks accurately in real-world contexts.
Polls, Surveys, and Real-Time Feedback Tools
Interactive polls and surveys allow learners to reflect on comprehension, provide feedback, and engage with the learning content in real time. During live blended courses at Singapore universities, instructors incorporated polls every ten minutes to assess learner understanding. These interactive checks improved attentiveness, allowed instructors to adjust pacing and content delivery instantly, and created a participatory learning environment where learners felt their input was valued.
Implementation Strategies for Interactive eLearning
Curriculum Design and Alignment
For interactivity to be effective, it must serve clear pedagogical objectives. Designers often align interactive elements with Bloom’s Taxonomy: quizzes reinforce recall, simulations promote application and analysis, and branching scenarios develop evaluation and decision-making skills. Each element must connect directly to learning outcomes, ensuring that interactivity is purposeful and contributes meaningfully to knowledge acquisition.
Balancing Complexity and Simplicity
While interactive content offers rich engagement opportunities, excessive complexity can frustrate learners. Effective design emphasizes intuitive navigation, minimal clicks, clear instructions, and logical content flow. Simplicity ensures accessibility, reduces cognitive overload, and allows learners to focus on the learning objectives rather than struggling with technology.
Accessibility and Inclusivity
Interactive content must adhere to WCAG accessibility standards, including providing transcripts for videos, alternative text for images, and keyboard-friendly navigation. Inclusive design ensures that learners with different abilities can access content fully, which is particularly important in diverse workplaces.
Localization and Cultural Sensitivity
Cultural relevance improves learner engagement. Scenario scripts, avatars, and contextual decisions should reflect local norms and workplace practices. Singapore-based organizations often localize global eLearning templates with Asian market scenarios, creating content that is more relatable, meaningful, and engaging for learners.
Strategic and Analytical Value of Interactivity
Driving Behavioral Change
Interactive eLearning is highly effective in promoting behavioral change. Learners can experiment with actions in simulations, observe outcomes, and reflect on their decisions. This iterative learning process builds behavioral memory, which is critical in compliance, leadership, and safety training. For instance, a Singapore healthcare regulator used interactive compliance simulations replicating inspection audits, and participants demonstrated 35% fewer non-conformance issues in actual audits, illustrating the tangible impact of interactive learning on workplace behavior.
Fostering Critical and Reflective Thinking
Interactive case studies require learners to analyze data, compare alternatives, and justify decisions. This cultivates reflective thinking, critical reasoning, and situational awareness—skills essential for leadership, management, and high-stakes decision-making. By encouraging learners to think beyond rote memorization, interactive learning prepares employees to tackle complex challenges in real-world environments.
Enhancing Data-Driven Insights
Every learner interaction—whether quiz attempts, scenario choices, or time spent on a module—produces valuable data. Learning analytics platforms aggregate this information to identify engagement trends, knowledge gaps, and course effectiveness. Organizations can leverage these insights to refine training strategies, target interventions, and demonstrate the return on investment of L&D programs.
Integration with Technology and Automation
Learning Management System (LMS) and LXP Integration
LMS platforms like Moodle, Docebo, and Cornerstone host interactive modules and track learner engagement. Advanced Learning Experience Platforms (LXPs) like EdCast and Degreed recommend personalized content based on user behavior, improving learner journeys and fostering continuous development.
Artificial Intelligence and Adaptive Feedback
AI-driven interactivity analyzes learner behavior in real time, adjusting content difficulty, recommending modules, and providing personalized feedback. If a learner struggles with specific scenarios, AI algorithms can assign additional exercises, ensuring mastery and bridging learning gaps.
Immersive Interactivity (AR/VR)
AR and VR bring immersive learning to life. Employees can navigate virtual environments, conduct simulated client meetings, or explore hazardous scenarios safely. This type of experiential learning enhances engagement, improves retention, and allows learners to practice skills that would otherwise be dangerous, expensive, or impractical in real life.
Cloud and Mobile Integration
Cloud-based delivery enables global scalability, while mobile-optimized content allows learners to access modules anytime and anywhere, including remote and field-based locations. For example, a Singapore logistics company deployed mobile-friendly interactive compliance checklists for warehouse staff, resulting in a 50% reduction in overlooked safety steps and improved operational adherence.
Enhancing Collaboration through Interactivity
Interactive eLearning also facilitates collaboration and social learning. Discussion forums, peer reviews, and group challenges encourage communication, teamwork, and collective problem-solving. Collaborative features replicate the benefits of classroom learning in a digital environment, fostering a sense of community and engagement among learners.
Measurement and Continuous Improvement
Key Metrics
Effectiveness is measured through engagement rates, knowledge retention, real-world application, and time efficiency. These metrics provide insights into learner behavior, content effectiveness, and the impact of interactive design on performance outcomes.
Continuous Refinement
Interactive modules should undergo continuous improvement through learner feedback, performance analytics, and compliance updates. Many organizations in Singapore follow a 12–18 month review cycle to ensure content remains relevant, accurate, and engaging, adapting to both technological advancements and regulatory changes.
Advantages of Interactive eLearning
Interactive eLearning enhances knowledge retention, drives learner engagement, and promotes behavioral accountability. Realistic scenarios and simulations improve compliance accuracy, while scalability allows thousands of employees to access content globally. Analytics enable continuous optimization, and inclusive design ensures all learners, regardless of ability, can participate effectively. Interactive learning fosters critical thinking, adaptive decision-making, and long-term skill application.
Conclusion to Interactive eLearning Content Boosting Knowledge Retention
Interactive eLearning transforms training from a one-way flow of information into an immersive, measurable, and behaviorally impactful learning experience. By integrating behavioral science, storytelling, and technology, organizations can achieve both engagement and retention—two pillars of effective workforce development. In Singapore’s progressive education and corporate training ecosystem, interactivity is not an optional enhancement but a core principle. It ensures that learners do more than just remember content—they understand, apply, and internalize it, bridging the gap between knowledge acquisition and lasting performance.