Brilliant eLearning Development Singapore: Role and Responsibilities
Brilliant eLearning Development Singapore: Role and Responsibilities
Introduction to the eLearning Developer Profession
The eLearning-related developer market has grown dramatically over the last ten years, driven by the digitalization of learning across education, professional training, and corporate programs. An eLearning developer is more than a content provider—they are multi-disciplinary professionals combining instructional design, technology, multimedia production, and user experience design to deliver effective online learning. This role demands both creativity and technical skill to meet a wide range of learning requirements aligned with organizational or institutional goals. Online education’s evolution has transformed eLearning development from a specialized tool into a mainstream approach for workforce training, higher education, and professional certification globally.
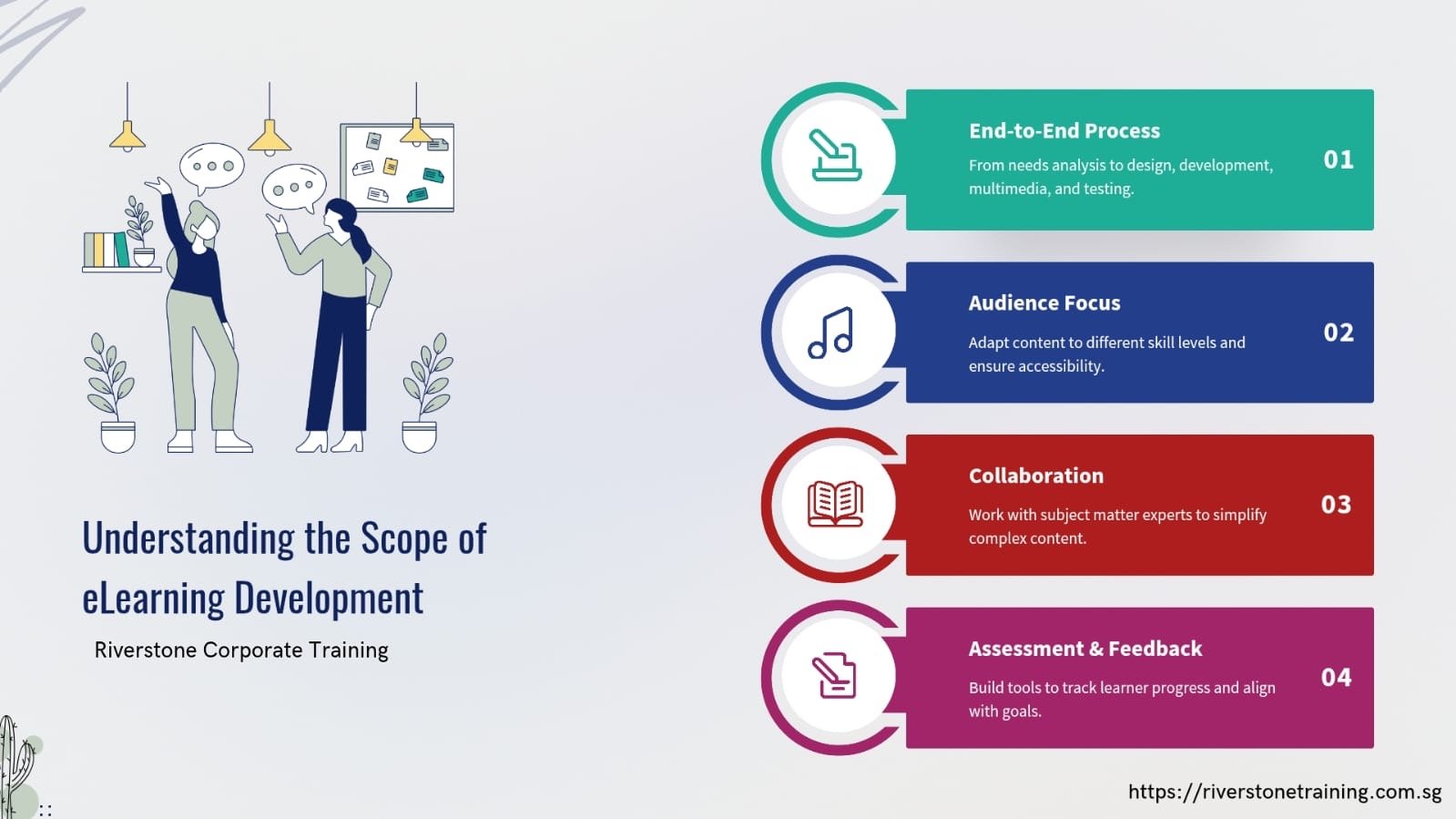
Understanding the Scope of eLearning Development Singapore
An eLearning developer’s role extends far beyond creating slides or uploading videos to a learning management system. They manage an end-to-end process, including needs assessment, analyzing learning objectives, designing instructional flow, developing interactive elements, integrating multimedia, and testing the final product. Developers must address diverse audiences, tailor content to varying skill levels, and ensure accessibility. Collaboration with subject matter experts ensures that content is accurate and digestible. Assessment tools and feedback mechanisms are embedded to track learner progress and align with course goals.
Core Responsibilities of an eLearning Developer
Being an eLearning developer requires both creative and high tech company Singapore expertise. Creatively, they brainstorm instructional methods, design storyboards, and define the learner journey from introduction to mastery, managing course pace, tone, and style. Technically, they develop interactive modules using authoring tools like Articulate Storyline, Adobe Captivate, or Lectora, and incorporate multimedia elements such as graphics, animations, voiceovers, and video. Quality assurance is essential to ensure content functions across devices, browsers, and LMS platforms, while troubleshooting and updating materials is ongoing as technology and organizational needs evolve.
Collaborating with Stakeholders and Subject Matter Experts
eLearning developers frequently work across teams with instructional designers, multimedia experts, learning strategists, and subject matter experts. Effective coordination ensures technical and content accuracy, transforming raw subject information into coherent learning narratives. Developers act as a bridge between technical teams and non-technical stakeholders, ensuring deliverables meet project objectives. Success in collaboration relies on interpersonal skills, flexibility, and the ability to provide and receive constructive feedback.
Technical Skills and Competencies Required
Professional eLearning developers must be proficient with a range of tools. Authoring tools enable interactive course creation, while graphic design and video/audio editing tools allow for visually. Knowledge product and services of eLearning of HTML5, CSS, and JavaScript supports customization and problem-solving. Familiarity with SCORM and other eLearning standards ensures LMS compatibility. Developers also integrate instructional design principles, user interface best practices, and accessibility standards to create inclusive, effective learning experiences.
Measuring Impact and Continuous Improvement
The work of an eLearning developer does not end once a course is released. Measuring effectiveness requires analyzing learner participation, assessment results, completion rates, and feedback. These insights guide iterative improvements to keep courses current, engaging, and effective. Continuous professional development—including staying updated on emerging technologies and best practices—is essential for delivering competitive eLearning solutions in an evolving digital learning environment.
Conclusion: The Strategic Importance of eLearning Developers
The strategic importance of eLearning developers in today’s rapidly evolving learning landscape cannot be overstated. Their role extends beyond technical execution to designing meaningful, engaging, and effective educational experiences. By combining instructional design, educational psychology, and technological skills, developers create courses that are scalable, adaptable, and aligned with learner needs. The rise of remote work, virtual classrooms, microlearning, and lifelong learning has amplified their importance in both educational and corporate contexts.
Through creative course design, intuitive interfaces, multimedia integration, gamification, and analytics-driven assessment, eLearning developers ensure learners remain motivated, retain knowledge, and apply skills in real-world contexts. They continuously adapt to emerging technologies like virtual reality, augmented reality, AI, and adaptive learning platforms, crafting personalized and immersive learning experiences. Their contributions enhance learning outcomes, knowledge transfer, and organizational efficiency, making them indispensable in the modern digital learning landscape. The combination of creativity, pedagogical insight, and technical proficiency makes eLearning development a dynamic, influential, and rewarding career, offering continuous growth opportunities and the chance to shape how people learn globally.